The Exercise Testing Laboratory offers three methods for evaluating health issues including cardiovascular fitness, aerobic endurance and performance, and pulmonary/cardiovascular health.
(1) Graded Exercise Testing (Treadmill and Bike)
Graded exercise testing is a critical tool in assessing cardiovascular fitness and aerobic endurance. One key measurement derived from this test is VO2 max, or maximal oxygen consumption, which quantifies the maximum amount of oxygen an individual can utilize during intense exercise. VO2 max is widely recognized as the gold standard for evaluating an individual’s cardiovascular and aerobic capacity.
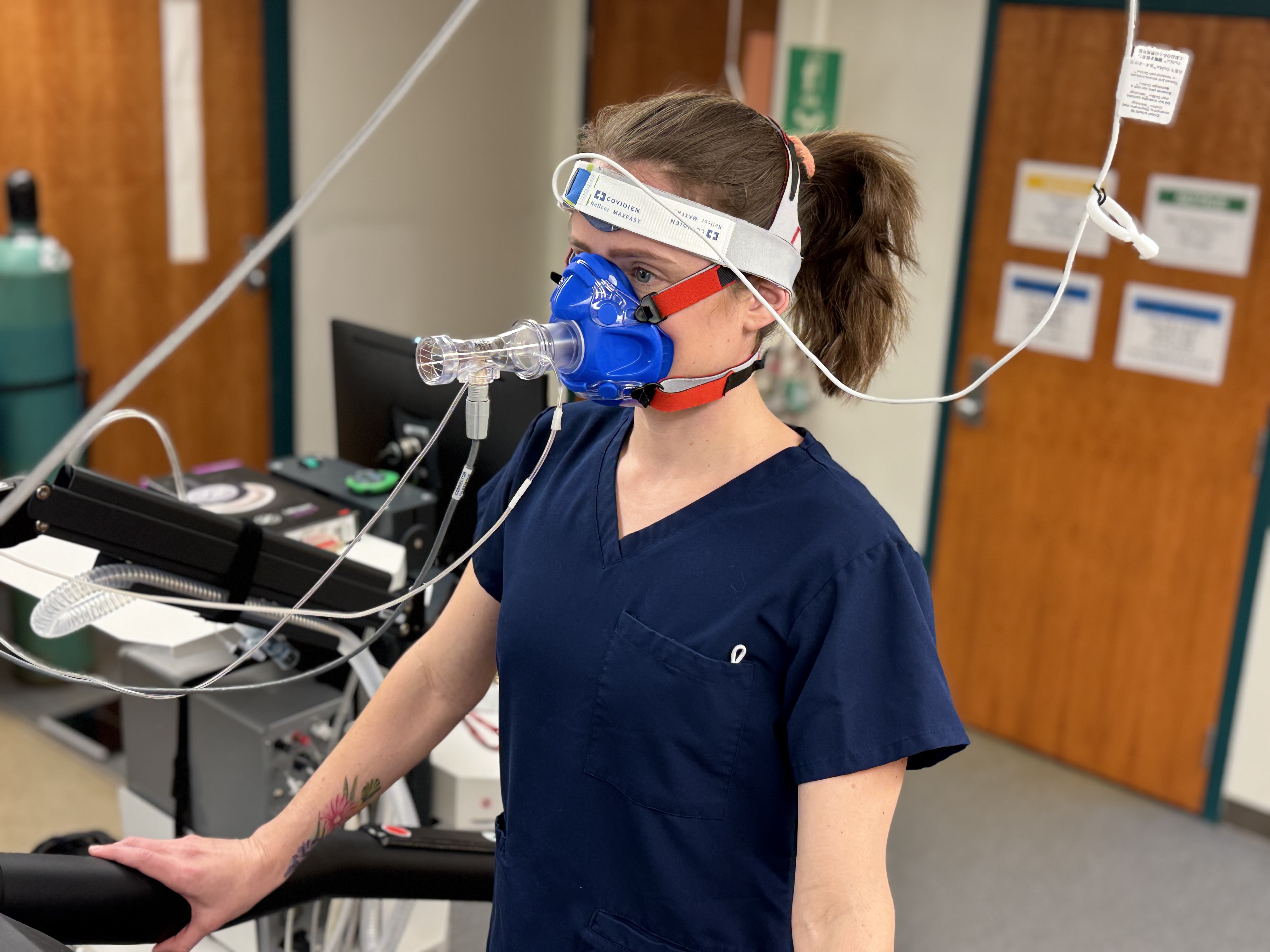 This test is typically employed in research settings to measure the effects of exercise interventions, new medications, or innovative device therapies. It is also used to monitor disease progression over time. Conducted on a treadmill or bike, graded exercise testing involves progressively increasing the intensity of the exercise to push the participant to their maximum physical limits.
This test is typically employed in research settings to measure the effects of exercise interventions, new medications, or innovative device therapies. It is also used to monitor disease progression over time. Conducted on a treadmill or bike, graded exercise testing involves progressively increasing the intensity of the exercise to push the participant to their maximum physical limits.
(2) Submaximal Exercise Testing (Treadmill and Bike)
The VO2 submaximal test is a variation of the VO2 max test, designed to estimate an individual's maximal oxygen consumption without requiring them to reach their absolute limit. This test is terminated once the participant reaches approximately 85% of their predicted maximum heart rate, making it a less invasive alternative.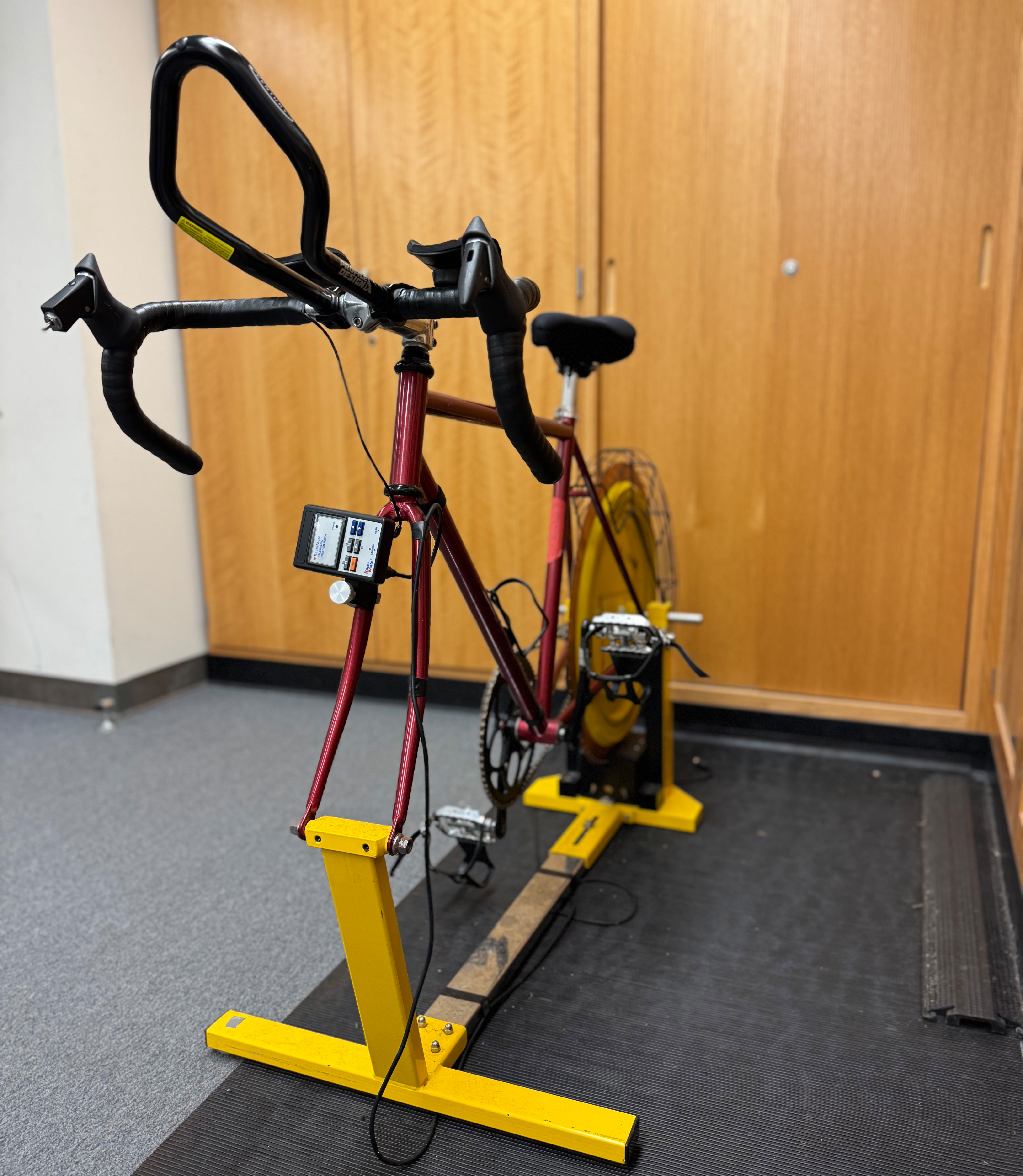 
Submaximal exercise testing is valuable for determining appropriate training zones, allowing for personalized fitness programs based on an individual’s estimated VO2 max. This test is particularly useful in scenarios where maximum exertion is not feasible or safe, such as with certain clinical populations or in general fitness assessments.
(3) Clinical Testing (Six-Minute Walk Test)
The 6-minute walk test, developed by the American Thoracic Society (ATS), serves as a practical method for evaluating a patient's endurance and aerobic capacity. This test provides insights into the functional performance of the pulmonary and cardiovascular systems.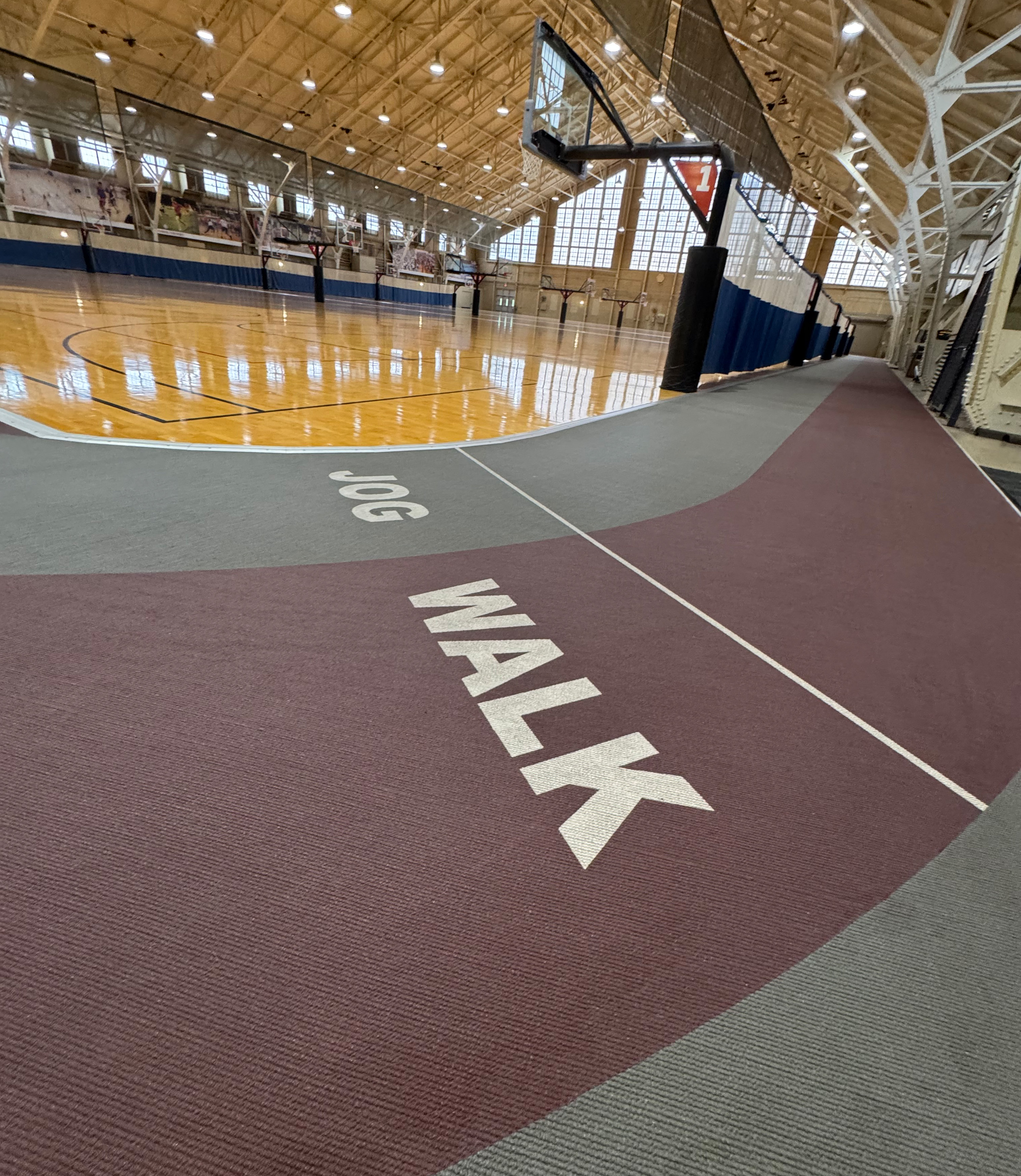 
During the test, the participant is instructed to walk back and forth between two fixed points for six minutes. Throughout this period, vital signs such as blood pressure and oxygen saturation are closely monitored to assess the body’s response to physical exertion.

